Basal cell carcinoma
Definition:
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells — a type of cell within the skin that produces new skin cells as old ones die off.
Basal cell carcinoma often appears as a waxy bump, though it can take other forms. Basal cell carcinoma occurs most often on areas of the skin that are often exposed to the sun, such as your face and neck.
Most basal cell carcinomas are thought to be caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight. Avoiding the sun and using sunscreen may help protect against basal cell carcinoma.
Symptoms:
Basal cell carcinomas usually develop on sun-exposed parts of your body, especially your head and neck. A much smaller number occur on the trunk and legs. Yet basal cell carcinomas can also occur on parts of your body that are rarely exposed to sunlight.
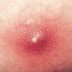
Although a general warning sign of skin cancer is a sore that won't heal or that repeatedly bleeds and scabs over, basal cell cancer may look like:
Some basal cell carcinomas may be difficult to distinguish from ordinary sores. See your dermatologist if you have:
Causes:
Basal cell carcinoma occurs when one of the skin's basal cells develops a mutation in its DNA. Basal cells are found at the bottom of the epidermis — the outermost layer of skin. Basal cells produce new skin cells. As new skin cells are produced, they push older cells toward the skin's surface, where the old cells die and are sloughed off.
The process of creating new skin cells is controlled by a basal cell's DNA. A mutation in the DNA causes a basal cell to multiply rapidly and continue growing when it would normally die. Eventually the accumulating abnormal cells may form a cancerous tumor.
Ultraviolet light and other causes
Much of the damage to DNA in basal cells is thought to result from ultraviolet (UV) radiation found in sunlight and in commercial tanning lamps and tanning beds. But sun exposure doesn't explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may contribute to your risk of skin cancer, such as being exposed to toxic substances or having a condition that weakens your immune system.
Complications:
Complications of basal cell carcinoma can include:
Definition:
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells — a type of cell within the skin that produces new skin cells as old ones die off.
Basal cell carcinoma often appears as a waxy bump, though it can take other forms. Basal cell carcinoma occurs most often on areas of the skin that are often exposed to the sun, such as your face and neck.
Most basal cell carcinomas are thought to be caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight. Avoiding the sun and using sunscreen may help protect against basal cell carcinoma.
Symptoms:
Basal cell carcinomas usually develop on sun-exposed parts of your body, especially your head and neck. A much smaller number occur on the trunk and legs. Yet basal cell carcinomas can also occur on parts of your body that are rarely exposed to sunlight.
Although a general warning sign of skin cancer is a sore that won't heal or that repeatedly bleeds and scabs over, basal cell cancer may look like:
- A pearly white or waxy bump, often with visible
blood vessels on your face, ears or neck. The bump may bleed, develop a
crust or form a depression in the center. In darker skinned people, this
type of cancer is usually brown or black.
- A flat, scaly, brown or flesh-colored patch on your back or chest. Over time, these patches can grow quite large.
- More rarely, a white, waxy scar. This type of basal cell carcinoma is easy to overlook, but it may be a sign of a particularly invasive and disfiguring cancer called morpheaform basal cell carcinoma.
Some basal cell carcinomas may be difficult to distinguish from ordinary sores. See your dermatologist if you have:
- A skin sore that bleeds easily or doesn't heal in about two weeks
- A sore that repeatedly crusts or oozes
- Visible blood vessels in or around a sore
- A scar in an area where you haven't injured yourself
Causes:
Basal cell carcinoma occurs when one of the skin's basal cells develops a mutation in its DNA. Basal cells are found at the bottom of the epidermis — the outermost layer of skin. Basal cells produce new skin cells. As new skin cells are produced, they push older cells toward the skin's surface, where the old cells die and are sloughed off.
The process of creating new skin cells is controlled by a basal cell's DNA. A mutation in the DNA causes a basal cell to multiply rapidly and continue growing when it would normally die. Eventually the accumulating abnormal cells may form a cancerous tumor.
Ultraviolet light and other causes
Much of the damage to DNA in basal cells is thought to result from ultraviolet (UV) radiation found in sunlight and in commercial tanning lamps and tanning beds. But sun exposure doesn't explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may contribute to your risk of skin cancer, such as being exposed to toxic substances or having a condition that weakens your immune system.
Complications:
Complications of basal cell carcinoma can include:
- A risk of recurrence. Basal cell carcinomas commonly recur. Even after successful treatment, they may recur, often in the same place.
- An increased risk of other types of skin cancer. A
history of basal cell carcinoma may also increase the chance of
developing other types of skin cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma
and melanoma.
- Cancer that spreads beyond the skin. Rare, aggressive forms of basal cell carcinoma can invade and destroy nearby muscles, nerves and bone. Very rarely, basal cell carcinoma can spread to other areas of the body.










0 komentar:
Posting Komentar